REGAINE® should only be used for the treatment of hereditary hair loss. Remember to always seek advice from a healthcare professional first, before treating any hair loss.
Hair Thinning
There are many ways to experience hereditary hair loss – you could be seeing high levels of shedding, or perhaps you’ve noticed a slightly receding hairline or less hair on the crown of your head.
But by far one of the most common symptoms of hereditary hair loss is hair thinning. This is when the hair gradually thins out over a fairly long period of time; it might not be immediately noticeable, but as it progresses it can become more obvious, and fairly distressing for those experiencing it. You might not see it falling out in clumps or visibly receding, but the volume of your hair will start to decrease and you might start to see less pigment in each strand.
So how do you know if your hair is thinning?
Spotting the signs
Thinning hair is often really tough to spot, because it doesn’t manifest with any of the more obvious indicators of hair loss. You probably won’t be pulling huge masses of hair out of your shower drain, and you most likely won’t develop any obvious balding spots straight away – hair thinning doesn’t cause mass shedding like this.
Instead, you might notice that your hair has a little less volume than usual. The texture of your hair might have changed slightly, becoming more weak and brittle when it should be healthy and thick. The pigment in your hair can also change – it might start to become lighter, with an almost translucent quality to some of your newly-grown hairs.
The science of ‘miniaturisation’
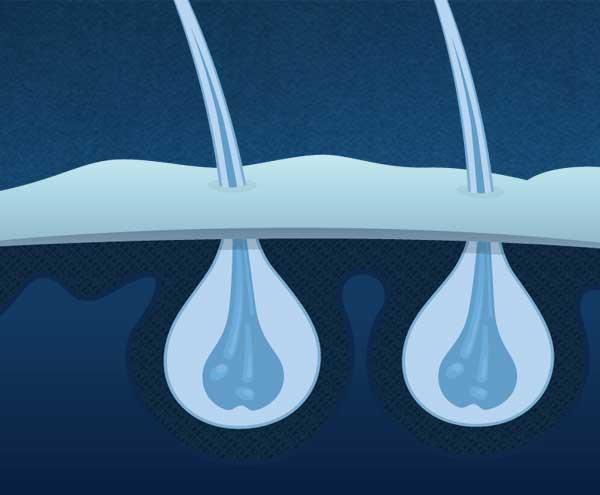
If your hair thinning is hereditary, it’s likely that your follicles are in the midst of a process called miniaturisation. This is when the male sex hormone dihydrotestosterone (also known as DHT - a more potent form of the regular testosterone that we all have in our bodies) attacks your follicles and causes them to slowly shrink over time. Whether or not you have an abundance of this hormone will be dictated by numerous factors including age, diet and lifestyle – but genetics will play the biggest role.
When your follicles are affected by an oversensitivity to DHT, they’ll start to slowly shut up shop. The hair cycle becomes shorter, so your hair spends less time in the growing phase. As you continue through the hair cycle numerous times over, the hairs that your follicles produce will become thinner, shorter and without as much pigment – until eventually the follicle shuts down entirely and stops producing hair.
Why does this happen?
If you’re experiencing hair thinning due to hereditary hair loss, it’s likely to be the result of a number of factors all working in tandem with one another. Genetics plays the biggest role in dictating the speed and scale of your hair loss, but age, hormones, diet and general lifestyle all play a part too.
You can look to your family for clues on how your hair thinning will progress over time – but it’s important to remember that they are just clues. You won’t get a definitive blueprint on how your hair thinning or loss will progress – that’s entirely personal to you and your own body.
Don’t forget…
Hereditary hair loss can be a challenging condition – but there are treatments available which can help. If you are looking for medicinal treatment options, remember to always talk to your pharmacist or healthcare professional first.